Playback time approx. 15 minutes
1 - Introduction
This work is the result of research on the Web and existing articles. What we're proposing is a pooling of our research to give you a better understanding of the project. The Web is undergoing an unprecedented technological transition: initially Web 1.0, now Web 2.0, and soon Web 3.0. This transition is profoundly transforming our relationship with the digital world.
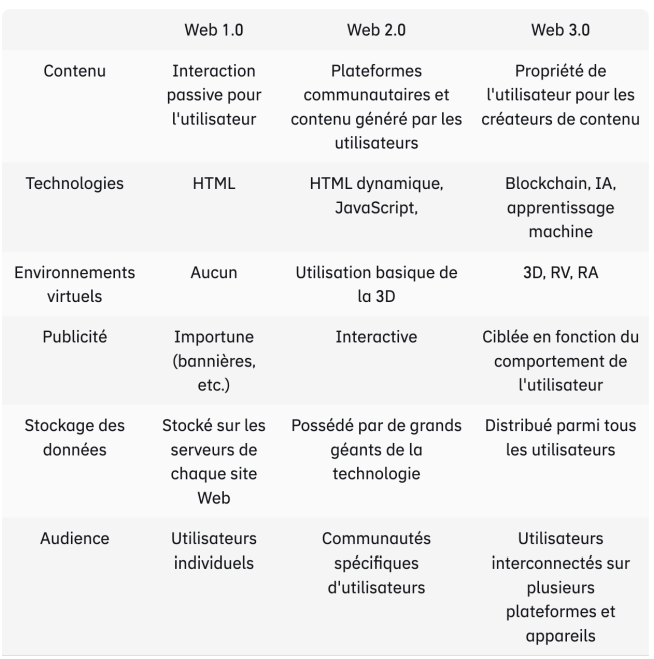
Web 3.0 is the third generation of Internet services for websites and applications. The aim is to offer a semantic Web based on machine understanding of data, with the aim of creating more intelligent, connected and open sites to offer a unique experience.
to each user.
2 - The history of Web 1.0 and 2.0
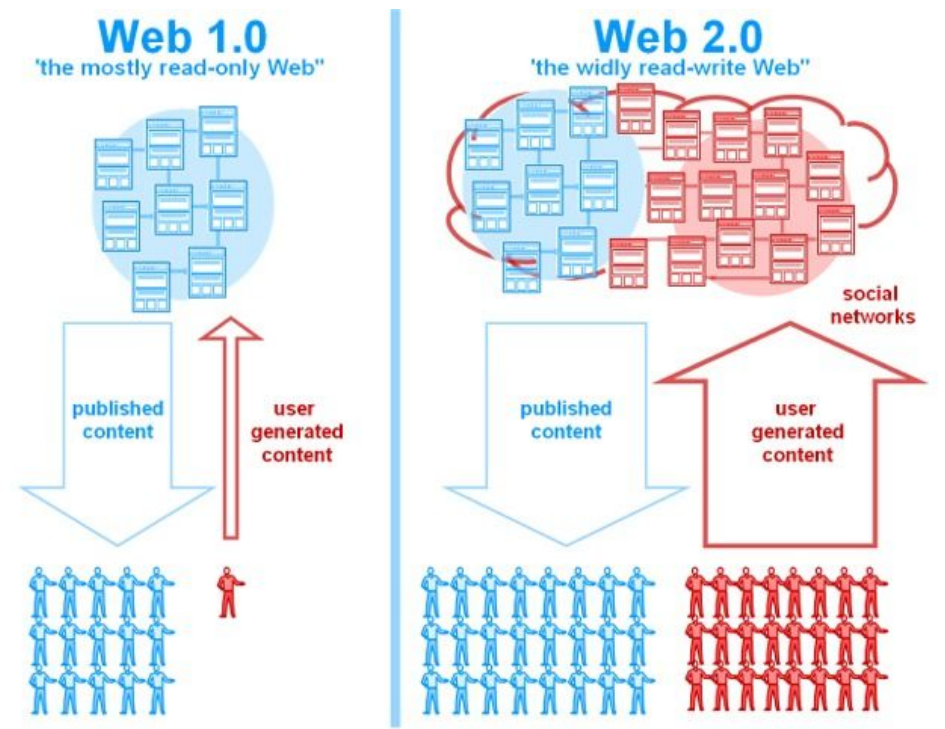
So far, we've experienced two major iterations of the Internet. The first, Web 1.0, marked the beginning of the Internet in the late 1980s, with "read-only" statistical web pages created by a relatively small number of participants. This was clearly a major advance, allowing anyone in the world to access published content.
But while users could read and browse these web pages, they couldn't interact with them much more than that. What's more, in the absence of search engines at the time, navigating the World Wide Web (WWW) was not the straightforward practice we know it to be today.
Thus, Web 1.0 is an information portal where users passively receive information, without being able to interact with it. By 2000, Web 2.0 was underway. Whereas the first iteration mainly involved a single flow of information from the Internet publisher to the Internet user, this new version enabled much greater user interaction and participation. Users can create their own accounts in various applications, which means they have their own unique identity in the online world. They are now able to interact.
This opened up enormous opportunities for business, particularly e-commerce, as new Internet companies could inexpensively market their products and services to a global base of potential online consumers. It also meant that anyone, anywhere in the world, could publish content for a global audience, giving rise to the globally popular blogging trend and fuelling user-published sites. And, of course, we mustn't forget the role of Web 2.0, which facilitated the rise of social media, first with sites like Myspace, then more explosively with Facebook, Twitter and YouTube, as the user-generated content revolution was in full swing.
Web 2.0 encourages participation, collaboration and information sharing. In short, Web 1.0 is about users being able to read content online, and Web 2.0 is about interaction between these different players.
3 - Web 3.0
3.1 - What is it?
Web 3.0 is the next generation of Internet technology that relies heavily on deep learning, a branch of artificial intelligence that uses data and algorithms to mimic the way humans learn, gradually improving its accuracy. It will also rely on blockchain technology to ensure the security of a decentralized Web. We're talking about a semantic Web.
The term was coined by Gavin Wood, founder of Polkadot and co-founder of Ethereum. Whereas Web 2.0 focused on user-created content hosted on centralized websites, Web 3.0 will give users greater control over their online data. This movement aims to create open, connected and intelligent applications and websites thanks to a better understanding of data by machines via deep learning. The result will be a Web experience that adapts to its user.
The decentralization and digital economies proposed by blockchain also play an important role in Web 3.0, as they enable us to attribute value to content created on the net. The result is a more immersive version of the Web.
3.2 - How it works
So, thanks to artificial intelligence, Web 3.0 will deliver personalized, relevant information faster, always with the aim of improving the user experience. This is made possible by search algorithms and the intelligent development of Big Data analytics, via which machines can intuitively understand and recommend content. Web 3.0 will also focus on content ownership and the support of digital economies accessed by users through the blockchain.
Today's websites generally display static information or user-driven content, such as forums or social networks. While this makes it possible to publish data on a large scale, it does not meet the specific needs of users. A website needs to adapt the information it provides to each individual user, just as human communication is dynamic in the real world. With Web 2.0, users lose ownership and control once this information is online.
3.3 - Benefits
Now that we've focused on decentralization and value creation in Web 3.0, as well as the role of artificial intelligence in the proposed user experience, let's look at the advantages this will bring in comparison with the static use of Web 2.0. The use of :
- Blockchain will eliminate the need for a central control point. Indeed, since
intermediaries are removed from the equation, they no longer control user data. This
freedom reduces the risk of censorship by governments or companies and reduces the effectiveness of
denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. This will also reduce the risk of data loss and
makes blockchain a serious competitor to the cloud. - A learning web via deep learning will lead to improved advertising and marketing by targeting specific audiences accordingly. Indeed, no one likes to be bombarded with online ads, however, if the ads are relevant to your needs, they can be useful instead of an annoyance. This is made possible by increased interconnectivity of information: as more and more products are connected to the Internet, larger data sets provide algorithms with more information to analyze. This can help them provide more precise information that meets the specific needs of each user.
This is the real power of combining deep learning via artificial intelligence with big data. We'll have more efficient browsing, moving from using search engines where finding the best results could be a challenge to more powerful search engines for finding semantically relevant results based on search context and metadata. The result is a more convenient Web browsing experience, making it easy for everyone to find the exact information they need.
Artificial intelligence will also enable better customer support. Customer support is essential to the smooth user experience of web sites and applications. However, due to the considerable costs involved, many web services are struggling to scale up their customer service operations. By using smarter chatbots that can talk to multiple customers simultaneously, users can enjoy a superior experience when working with support agents.
4 - The main characteristics of Web 3.0
To sum up, if Web 3.0 is to deliver the innovative services it proposes, it will need to take into account 4 key perspectives in order to offer the best possible use to its users.
- Semantic markup : Over time, machines have improved their ability to understand
data and content created by humans. However, creating a seamless experience where semantics are fully understood will take time. For example, the use of the word "bad" can, in some cases, mean "good". For a machine, this can be incredibly difficult to understand. However, with Big Data and other information to study, AI is beginning to better understand what we write on the Web and present it intuitively. - Blockchain and cryptocurrencies: Data ownership, online economies and decentralization are key aspects of Gavin-Wood's Web 3.0 future. Blockchain
offers an approved system for achieving many of these objectives. The power for anyone to
tokenize assets, put information on a blockchain and create a digital identity is a great innovation that lends itself to Web 3.0. - 3D visualization : In other words, the appearance of the Web will change radically. We
we're already seeing a transition to 3D environments that even incorporate virtual reality. Visit
metavers is one of the pioneers of these experiences, and we are already familiar with encounters through 3D video games. The fields of user interface and user experience also make it possible to present information in a more intuitive way for web users. - Artificial intelligence: Artificial intelligence is the key to transforming content created by
into machine-readable data. We already know about customer service robots,
but that's just the beginning. AI can present us with data and sort it, making it a useful tool.
for Web 3.0. Best of all, the AI will learn and improve itself, reducing
the work needed for human development in the future.
Thanks to these 4 points, a user can have a unique experience, optimized according to his needs and profile. He'll have a digital identity with which he'll have purchasing and development power. They'll enjoy a more immersive experience, thanks to technological advances in 3D visualization.
5 - Web 3.0 and cryptocurrency
Blockchain and cryptocurrency have great potential when it comes to Web 3.0. Decentralized networks are successfully creating incentives for more responsible data ownership, governance and content creation.
The most relevant aspects of Web 3.0 include :
- Decentralization : the transparent dissemination of information and power across a vast set of people is simple with blockchain. This contrasts with Web 2.0, where the big tech giants dominate vast swathes of our online lives.
- The use of digital cryptocurrency wallets: anyone can create a wallet that enables them to carry out transactions and act as a digital identity. You don't need to store your information, nor create an account with a centralized service provider. You have total control over your wallet, and often the same wallet can be used on multiple blockchains.
- The digital economy: The ability to own data on a blockchain and use decentralized transactions is creating new digital economies. They enable us to easily value and exchange goods, services and content online without having to provide banking or personal data. This openness helps improve access to financial services and enables users to start earning money.
- Interoperability: DApps and blockchain data are becoming increasingly compatible. Blockchains built using the Ethereum virtual machine can easily support DApps, wallets and tokens from different blockchains. This enhances the ubiquity needed for a connected Web 3.0 experience.
6 - Web 3.0 today
6.1 - Artificial intelligence
It's interesting to realize that the use of artificial intelligence and deep learning in Web 3.0 isn't just about analyzing data from individual users.
Take Apple's Siri and Amazon's Alexa, both of which offer virtual assistants that tick most of the Web 3.0 boxes. AI and natural language processing help both services better understand human voice commands. The more people use Siri and Alexa, the more their AI improves its recommendations and interactions. This makes them a perfect example of a semantically intelligent Web application that belongs in the Web 3.0 world.
6.2 - Connected smart home
One of the key features of Web 3.0 is ubiquity. This means we can access our data and online services on multiple devices. The systems that control your home's heating, air conditioning and other energy sources can now do so intelligently and connected. Your smart home can know when you leave, when you arrive and how much you like the heat or cold in your home. It can use this information, and much more, to create a personalized experience. You can then access this service from your phone or other online devices, wherever you are.
7 - Conclusion
The evolution of the Internet has been a long journey, and will surely continue into new iterations. With the massive explosion in available data, websites and applications are evolving towards a more immersive, user-specific Web experience. Although there's still no concrete definition of Web 3.0, innovations are already on the move. We're on the road to a semantic Web, a Web that will offer a unique, personalized experience to each user, based on the analysis of their data.
However, issues of latency, scale and reliability remain challenges in the transition to Web 3.0, and companies that aspire to improve the Internet will help resolve these issues, while stimulating wider adoption of DApps and the decentralized Web. The positive effects on the network resulting from increased adoption will continue to amplify the benefits of Web 3.0, which in turn will lead to increased adoption.
